This is something very basic but thought of sharing with beginners.
Here is something that I have tested and works absolutely fine.
- KVM is an opensource Type 2 hypervisor installed on Linux machines.
Below mentioned is the procedure to setup KVM in a virtual Environment (VMWare Workstation)
_________________________________________________________________________________
Step 1: Install kvm
terminal# apt-get install qemu-kvm libvirt-bin virtinst bridge-utils cpu-checker
_________________________________________________________________________________
Step 2: Verify kvm installation
Ideally the output should be:
terminal# kvm-ok
INFO: /dev/kvm exists
KVM acceleration can be used
If you come across something like this :
INFO : Your CPU does not support KVM extensions
KVM acceleration cannot be used
terminal# ls -l /dev/kvm
ls: cannot access ‘/dev/kvm’: No such file or directory
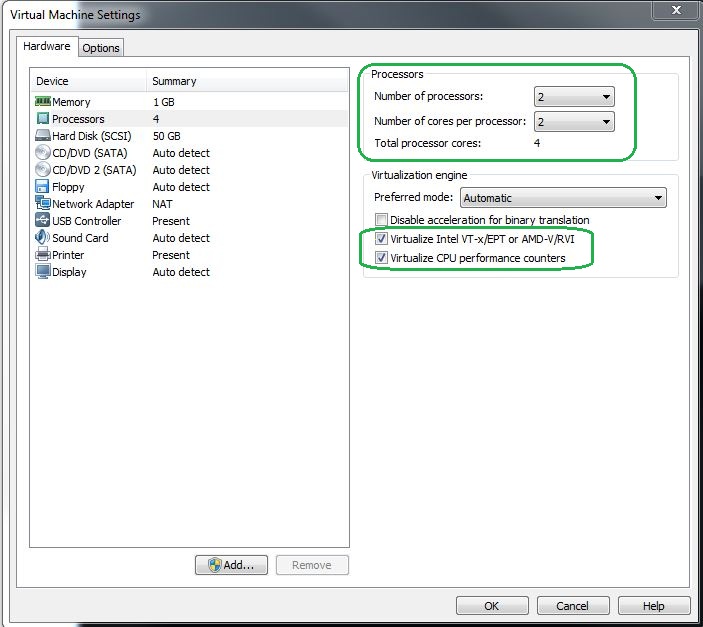
Make the following changes on the workstation :
Start the server again and execute the command “terminal# kvm-ok”.
INFO : /dev/kvm exists
KVM acceleration can be used
_________________________________________________________________________________
Step 3 : Check libvirtd status : For QEMU/KVM to connect you need to have libvirt daemon active.
terminal# systemctl status libvirtd
If libvirt daemon is not active, you need to manually start the service using the following command :
terminal# systemctl start libvirtd
_________________________________________________________________________________
Step 4 : Working on getting the GUI access : Need to install virt-manager
terminal# apt-get install virt-manager
To open the GUI :
terminal# virt-manager
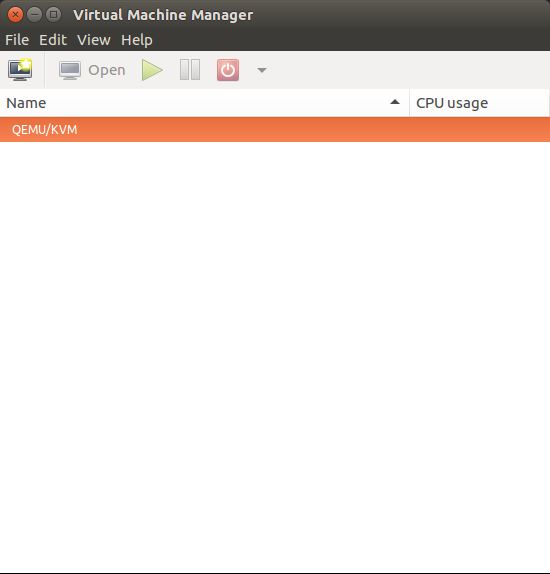
This is what a KVM looks like :
That is all. KVM should work absolutely fine.
Note :
- To deploy PA you need to allocate RAM > 4 GB.
- Also make sure that you configure bridged network on Ubuntu before installing PA. (I will share the details sometime later about the same. This email is just to make you guys aware of KVM)
- Installing KVM on Kali Linux is bit tricky as kali cannot find libvirt-bin in its repository (Please stick to Ubuntu Server 14 TLS).